1) testes
* produces sperm
* produces testosterone (male
sex hormone) which:
a)
regulates the maturation of sperm
b) development of secondary sex characteristics such as facial hair
and a deeper voice
* the testes are
located in the scrotum outside the internal body cavity to keep
the testes 1-2 degrees Celsius cooler than the body for the optimum
temperature for producing and storage sperm
2) glands
and tubes
* sperm are produced in the testes and are stored in the tube called
the epididymis
* they are then carried through the abdominal cavity by the tube
called the vas deferens which...
* connects with the urethra (leads out of the penis)
* along the way through the tubes, certain glands add fluids to
the sperm to nourish them and protect them from the acidic environment
of the woman's vagina such as:
a)
prostrate gland
b) seminal vesicles
c) Cowper's gland
* these secretions
and sperm are referred to as SEMEN as is released during ejaculation
3)
penis
* an adaptation for internal fertilization
gets the sperm up into the female's reproductive tract
B) Female Reproductive
System
* carries
out oogenesis; the production of one viable
monoploid (usable) egg and 3 non-viable polar bodies from one
primary sex cell
* produces many hormones, including estrogen
and progesterone which:
a)
control menstrual cycle
b) development of secondary sex characteristics, such as development
of mammary glands (breasts) and the broadeneing of pelvis (hips)
OVULATION:
when eggs are matured and released
2) oviduct
* after ovulation, the egg is transported through the oviduct
(a.k.a. Fallopian tubes) heading towards the uterus
* if the egg is to be fertilized, it happens in the oviducts
3) uterus
* where the embryo implants if development occurs
* at the lower end of the uterus is the cervix, which leads to the
muscular tube called the vagina
* the vagina is opening between the internal and external environment
II.
The Menstrual Cycle
* begins at puberty and ends at menopause (which is a
permanent cessation (stoppage)
* usually lasts approximately 28 days
* can vary a great deal due to:
1) age
2) illness
3) pregnancy
4) stress
5) other factors

* there
are 4 stages to the menstrual cycle:
A) follicle stage:
* FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone),
produced by the pituitary (of the endocrine
system) tells the egg to mature
* estrogen is produced from the
ovary to build up the uterine lining
(blood vessels) in case the embryo implants AND to stimulate ovulation * ~days 1-14 of the cycle
NEGATIVE
FEEDBACK
as the estrogen levels get higher, the pituitary
inhibits (slows) its production of FSH and stimulates (speeds up)
the production of LH (luteinizing hormone);
this leads to...
B) ovulation:
* the mature egg is released from the follicle around day 14
* the high levels of LH (luteinizing hormone) stimulates the ruptured
follicle to transform into the corpus luteum
C) corpus luteum
stage:
* the newly formed corpus luteum (in the ovary)
now secretes progesterone which
will prepare the uterine lining for possible fertilization/implantation
* ~days 14-26 of the cycle
III.
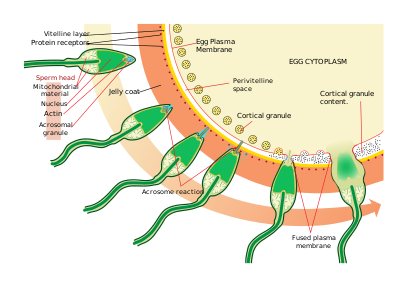
Fertilization in Humans
* happens internally
* after ovulation, fertilization usually occurs in the oviduct (Fallopian
tubes)
* if not fertilized within ~24 hours, the egg deteriorates and can
no longer be fertilized
* cleavage begins in the oviduct
* ~ 6-10 days later, the developing embryo (now a blastula) may be
implanted in the lining of the uterus
* gastrulation and differentiation occur after the embryo has been
implanted in the uterine walls
* if
more than one egg is produced, you can have more than one embryo
FRATERNAL
TWINS result when 2 eggs are fertilized by
2 different sperm cels
IDENTICAL
TWINS result with 1 egg gets fertilized by
1 sperm; during cleavage, the zygote breaks off into two completely
separate cells
* external
fertilization- fusion of gametes OUTSIDE the mother's reproductive tract
as in...
* in vitro fertilization-
where an egg (ovum) and sperm are fused externally and the embryo is
then implanted artificially into the mother (test tube baby)
IV.
Human Development
* the time between fertilization and birth is referred to as the gestation
period
* in humans, the gestation period is about 9 months* at the end of the gestation period, the secretion of progesterone
from the ovary decreases and another hormone from the pituitary gland
causes the females body to go into labor
A) Pre-Natal
Development
* development
before birth
* the first 2 months are the most important--this is when the cells
become specialized--differentiation
* MANY THINGS CAN GO WRONG!!!
* there is a 5% chance that the developing embryo/fetus can have
some sort of DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITY automatically, without any
other influences
* the number can go up depending on many factors such as:
1) genetic
problems
* defective genes and/or chromosomes that often runs through families
* these are present at conception (fertilization)
2) acquired
problems
* problems that can be prevented!
a)
drug, alcohol, and tobacco abuse
* leads to low birth weight (less than 5 pounds at birth), which
is the leading cause of developmental disability--lots of problems
* possible cerebral palsy, seizure disorders (epilepsy), immature
organs (heart, liver, kidney), RDS (respiratory distress syndrome),
non-developed immune system
THIS
CAN BE PREVENTED! IF YOU ARE PREGNANT, DON'T LET CHEMICALS GET INTO
YOUR BLOOD WHICH CAN THEN GET INTO YOUR DEVELOPING CHILD'S BLOOD
b)
maternal/paternal factors
c) STD's (sexually transmitted diseases)
d) mother nature
e) poor prenatal care
* mother doesn't go to the doctor
* bad diet (caffeine and any other chemicals)
f) teenage parents
* your bodies are not fully developed yet, so what are the chances
that the children of the children will be healthy?
B) Post-Natal
Development
*
development after birth
* happens at different rates until the person is a mature adult, where
it slows down, until eventually death...? what about telomeres? or
aging genes turned off? ...who wants to live forever?
aging--
the complex developmental changes that occurs naturally, with the passage
of time
 labia reduction is becoming more popular as acceptance of cosmetic and
reconstructive vaginal plastic surgery becomes mainstream thought. Labia
reduction surgery and vaginal tightening or vaginal rejuvenation are
becoming as nearly as common today as other cosmetic surgeries,
including breast implants and rhinoplasty. New advances in labioplasty
and vaginoplasty have lessened the pain, scarring
labia reduction is becoming more popular as acceptance of cosmetic and
reconstructive vaginal plastic surgery becomes mainstream thought. Labia
reduction surgery and vaginal tightening or vaginal rejuvenation are
becoming as nearly as common today as other cosmetic surgeries,
including breast implants and rhinoplasty. New advances in labioplasty
and vaginoplasty have lessened the pain, scarring